ch6 - Activation Record¶
Compiler 应该将所有 code 翻译为汇编语言,并为 data 分配空间。

首先来回顾一下现代处理器架构:
-
ALU 算术逻辑单元( operands 可为 immediate,register & memory)
-
Control(用于执行指令,因为instruction在内存中,靠PC标识)
-
Register
-
Memory(注意stack向下增长,heap向上增长)

这一章集中于 Stack,也就是 Activation Record 处在的地方:

Activation Record 要解决的问题就是 Function call 时的记录,重点为 Application Binary Interface:
- Contracts between binary programs
- Even compiled from other languages
- Conventions on low-level details
- How to pass arguments?
- how to return values?
- how to make use of registers?
1. Stack Frame¶
Stack Frame 即 Activation record,是 a piece of memory on the stack for a function,它连接了 caller 和 callee :
- Relevant machine state (saved registers, etc.)
- Space for return value
- Space for local data
- Pointer to activation for accessing non-local data

如何设计让 caller 和 callee 正确且高效沟通?
- Frame pointer (FP) 帧指针, “基址寄存器(base pointer)” 指向当前函数栈帧的基址
- Stack pointer (SP) 栈指针,指向栈顶

x86中,rbp 存FP,rsp存SP;先将上一个frame的FP值push进栈,再将当前 SP 赋给 rbp,作为 current frame的FP。rdi 存函数传递的参数。rax将存函数返回值。
当函数 f 调用函数 g 时,SP 指向 f 传递给 g 的第一个参数,g 通过从栈指针减去栈帧大小来分配自己的栈帧;当进入函数 g 时,将旧的帧指针 FP 保存在内存中,设置 FP = SP,使 FP 指向当前栈帧的基址;当函数 g 退出时,设置 SP = FP,恢复栈指针,从保存的位置获取旧的 FP 值(pop rbp)

- Globals 不能被存在栈中,All references to a global variable point to the same object,Globals are assigned a fixed address once,所有 “fixed address” 都是 “statically allocated”
- 动态分配的数据被存在 Heap 中,因为这些数据的生命周期可能比创造它们的 blocks 更长,故不能存在 activation record 中
2. Use of Register¶
Putting everything in the stack frame can cause the memory traffic,解决方法为 Hold as much of the frame as possible in registers,下述 value 可以保存在寄存器中:

2.1 Parameter Passing¶
Tiger的参数方式: Call-by-value
- 实参(actual arguments)的值被传递并作为形式参数(formal parameters)的值。
- 形参的改变不会影响实参
如果在 stack 中进行参数传递,会导致 memory traffic。所以前 k 个 arguments ( k = 4 or 6) 通过寄存器传递(X86-64: rdi, rsi, rcx, rdx; ARM:r0~r3),剩余参数通过 stack 传递。
保存寄存器状态的需求:

两种保存方式:caller-save 和 callee-save

caller-save例:

callee-save例:

总结:

如果 f 在用rdi传参前,要先把rdi当前的值存入stack frame(调用完再恢复) , 那最终并没有避免stack frame的访存操作(导致memory traffic)!

如何解决类似上图的 memory traffic 呢?
- 在调用h后a的值不再使用(不存在第5行),这样就不用保存寄存器r1的值了。这可以通过优化代码做到。
- Use global register allocation: different functions use different set of registers to pass arguments. 如f可用寄存器r1接收参数,但通过寄存器r2给h传参
- Leaf procedures:不调用其他过程的为叶子过程(Leaf procedure)。叶子过程不必将传入的参数保存到存储器中。parameters of leaf procedures can be allocated in registers without causing any extra memory traffic
- Use register windows (as on SPARC): Each function invocation can allocate a fresh set of registers
2.2 Return Address¶
当调用函数 f,f 需要知道返回到哪个位置
- Old approach (1970s): Push return address on stack via call instruction
- Modern approach: Put return address in a designated register (e.g., rip 指令指针寄存器)
2.3 Return Value¶
Placed in designated register by callee function.
- X86-64系统整型返回值:rax

2.4 Locals and Temporaries¶
- (Some) Local variables
- (Some) Intermediate results of expressions (temporaries)

更多细节将在 register allocation section 讨论。
3. Frame-Resident Variables¶
既然很多地方都可以用寄存器,那还需要在stack frame中分配内存空间吗?
答案肯定是要,因为:
- 变量 passed by reference , 需要一个内存地址来传递,故存在栈帧中

- Its address is taken, e.g., &a in the C language

- 变量需要通过一个嵌套结构获取

- The value is too big to fit into a single register

- 变量是 数组 ,for which address arithmetic is necessary to extract components (但是这种情况下放在栈帧还是heap上值得讨论)

- The are too many locals and temporaries – “spill”(于寄存器分配章节中讨论)
前三种情况可以看作 “variable escapes”:

4. Block Structure¶
我们可以通过帧指针访问局部变量(注意,FP的实际值在运行时是未知的,但是每个局部变量相对于FP的偏移在编译时是已知的!)
problem:How can h access the “non-local” variables m?
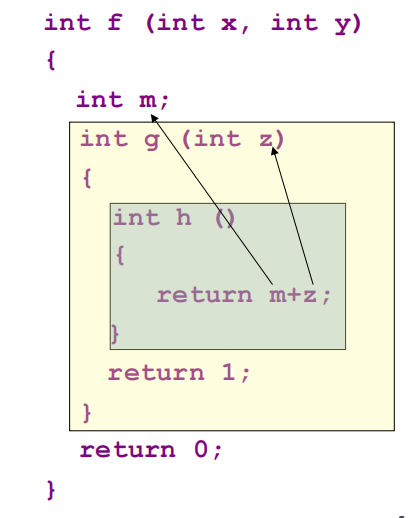
4.1 Static Link (重点)¶
The static link is a pointer to the activation record of the enclosing procedure.
每当 f 调用 g 时,它都会传递指向 f 的最近一次 activation record 的指针,该记录立即 encloses g in program text
如何利用 static links 获取 non-local data:
- Each function is annotated with its enclosing depth
- When a function at depth n accesses a variable at depth m: Emit code to climb up n-m links to visit the appropriate activation record


- pros: 参数传递的额外开销较少(每个 activation record 只需要一个额外的指针)
- Cons : O(n) time to access a variable n levels up.

在x86-64架构中,动态链接就是函数序言中保存的旧rbp值(push rbp后存储在栈上的那个值)。而静态链接通常存储在[rbp+8]位置。
4.2 Display (可能重点)¶
Display 是 a global array of pointers to frames
- 该全局指针包括每一个词法 level 的 frame pointers
- Array[i] = pointer to most recent activation at level i (同 leve l可能有多个函数,取最 recent 的)
- Update display when entering/exiting a function(难点)
- 可直接获取,不需 chain traversal



push、pop的栈和函数栈帧共用一个栈?
- Pros:O(1) access time to any lexical level; Simpler code generation
- Cons:Complex context switching; Display array is a global resource

4.3 Lambda Lifting¶
- 对每个函数,identify 函数用到的所有 non-local variables
- 将这些变量作为函数的 extra parameters
- Update all calls to pass the required variables
当 g calls f,g 的所有变量都会被 f 获取(or by any function nested inside f),传递给 f 作为 extra argument.

Pros:
- Simplified runtime environment: No need to maintain complex stack frames with static links or displays.
- Optimization opportunities: Makes data flow explicit through parameters, etc
Cons:
- Performance overhead: Passing multiple extra parameters increases call overhead (unnecessary passing when the variables aren't used)
- Limited applicability: Not always suitable for higher-order functions
6. A Typical Stack Frame Layout for Tiger¶

关于 incoming argument(由caller传递) 和 outgoing argument(传递给将要调用的函数)的一个具体例子:
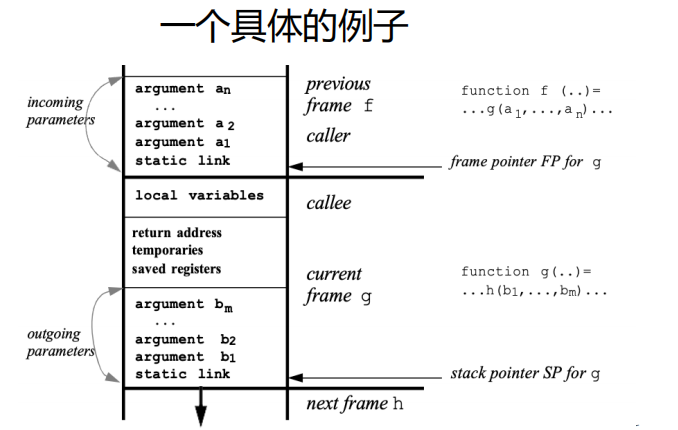
- Frame point为特定寄存器(如rbp,SP),其值为栈上的内存地址,内存地址中保存的值为
stack link (某个函数的frame point)
- Return address: where (within the calling function) control should return(通过CALL指令创建)
Limitation:
